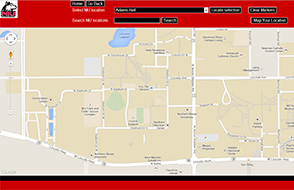
There are two data formats in particular that are commonly found in interactive web maps: GeoJSON and SVG. GeoJSON is an open format for encoding a variety of geographic data structures, while Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) is an XML-based vector image format for 2D graphics that supports browser interactivity and animation. GeoJSON is highly compatible with the Leaflet mapping library. SVG is similarly compatible with the Raphael.js and Kartograph.js libraries. Links to examples of maps using both data formats can be found below.
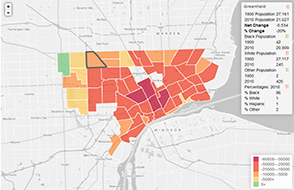
1. Save shapefile in ArcGIS and export to shp folder.
2. Zip all files associated with the shapefile into a separate folder.
3. Using this converter tool, browse to the zipped folder and hit Convert to GeoJSON.
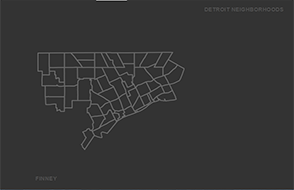
1. Save shapefile in ArcGIS and export to shp folder.
2. Open shapefile in QGIS and export to SVG using Print Composer (use add map icon, then export to SVG icon).
3. You can now visualize the SVG file in Notepad++.
4. Open the SVG file in Illustrator or Inkscape (open source) and make edits.
5. Save the file and export out as SVG.
6. Download Raphael.js.
7. Place the paths for each shape into your html. Example
1. Web Map Service: The Standard That Isn't
5. Storing GIS Data for the Web
8. SDI-in-a-Box: Web Mapping Frameworks
© 2014 Mike Ribant